During Anaerobic Respiration Glucose Molecules Are Converted Into Molecules of
Thus when 20 molecules of glucose will break down anaerobically they will produce 40 molecules of ATP. Aerobic cell respiration glycolysis the Krebs cycle respiratory electron transport produces 36 ATPglucose consumed.
Anaerobic respiration is a form of respiration that does not require oxygen and can occur in animals plants and other microorganisms.

. Glycolysis produces only two net molecules of ATP per 1 molecule of glucose. Hence organism A can convert glucose into alcohol. A 6-carbon glucose molecule of glucose still splits into.
Anaerobic cell respiration glycolysis fermentation produces 2 ATPglucose consumed. That glycolysis is the first step of aerobic respiration and is the only energy-producing step in anaerobic respiration. In animals where there is sufficient oxygen supply pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide.
See answer 1 Best Answer. As a result of anaerobic metabolism in cells glucose isconverted in the cytoplasm to lactic acid without employing theelectron transport change. A Both the statements are individually true and the Statement II is the correct explanation of the Statement I.
It is the fermentation process where pyruvate is produced at the end of glycolysis and is converted to lactate by the lactate dehydrogenase enzyme. During aerobic respiration glucose is oxidized into two pyruvate molecules. During glycolysis glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid.
In the electron transport chain exergonic redox processes drive the endergonic reaction in which. In the absence of oxygen it enters the anaerobic respiration where it is converted to lactate. In anaerobic respiration one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of ethanol in yeast or lactic acid in muscle cells with a net gain of two molecules of ATP adenosine triphosphate.
Glycolysis in anaerobic respiration is similar to that in aerobic respiration. That glycolysis breaks down glucose 6 carbons into 2 3-carbon pyruvate molecules and that the energy reward for this is ATP and. During anaerobic respiration carbohydrates in the form of glucose are broken down into two molecules of pyruvates and 2 molecules of ATP are generated.
In the process of anaerobic respiration a single molecule breaks down to produce 2 molecules of ATP. Hydrogen carriers NADH from an oxidised precursor NAD A small yield of ATP net gain of 2 molecules. How this actually happens one molecule of glucose is broken in half into two 3-carbon molecules because glucose is a 6-carbon molecule so 6 split in half is 3 But this needs energy to happen so 2 ATPs that were made in the past must be used to give the energy to split glucose.
So Under aerobic conditions the net formation of ATP until the formation of pyruvate is 2 ATP 1 NADH 3 ATP 5 ATP. Lactic acid fermentation In this type of anaerobic respiration glucose is split into two molecules of lactic acid to produce two ATP. Statement I Two ATP molecules are produced during anaerobic respiration.
Relative to oxidative phosphorylation which maximizes the energy potential of a single glucose molecule approximately 32 molecules of ATP per 1 molecule of glucose glycolysis is an inefficient means of energy production. During cellular respiration glucose is converted into two pyruvic acid molecules. All of the choices are correct.
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and is an anaerobic process. It is the process whereby the cellular breakdown of carbohydrates takes place in the absence of oxygen. Two molecules of carbon dioxide are released as the byproduct.
Anaerobic respiration without oxygen During glycolysis glucose molecules six-carbon molecules are split into two pyruvates three-carbon. It is a type of anaerobic respiration where sugar molecules glucose and other six-carbon sugars are metabolized to lactate releasing the chemical energy in the form of ATP molecules. This process also produces two ATP.
During anaerobic cellular respiration glucose is broken down without oxygen. Are each converted into a two-carbon molecule joined to a coenzyme A molecule. Thus during aerobic respiration one glucose molecule gives 233 molecules of ATP in glycolysis only.
In fermentation instead of carbon dioxide and water lactic acid is produced which can lead to. It helps in regenerating the NAD lost in the process of glycolysis. Glycolysis breaks down glucose 6-C into two molecules of pyruvate 3C and also produces.
It occurs in certain types of bacteria and some animal tissues such as muscle cells. Statement II Glucose is converted into pyruvic acid through a series of reactions with a net gain of 2 ATP molecules. The process of anaerobic respiration converts glucose into two lactate molecules in the absence of oxygen or within erythrocytes that lack mitochondria.
Instead organic or inorganic molecules are used as final electron acceptors. It only occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. What is glucose broken down into during anaerobic respiration.
A glucose molecule that is metabolized via aerobic respiration has been completely broken down and released as CO2 by the end of. Anaerobic respiration has two stages. In anaerobic conditions there is no conversion of NADH to ATP.
There is lactate production in animals and ethanol plus carbon dioxide in plants. This happens in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration. Together contain less chemical energy than was found in the original glucose molecule.
The pyruvate enters mitochondria and is reduced to carbon dioxide. Click to view a larger image. The chemical reaction transfers glucose energy to the cell.
That cell respiration is the process of gradually breaking down glucose and collecting usable energy from it. What is anaerobic in cellular respiration. Thus the ATP molecules produced in anaerobic.
The citric acid cycle. Yeast behaves like organism A. During the respiration of an organism A 1 molecule of glucose produces 2 ATP molecules whereas in the respiration of another organism B 1 molecule of glucose produces 38 ATP moleculesa Which organism is undergoing aerobic respirationb Which organism is undergoing anaerobic respirationc Which type of organism A or B can convert glucose into alcohold.
Alcoholic fermentation In this type of anaerobic respiration glucose is split into ethanol or ethyl alcohol. In the presence of oxygen the pyruvate molecules would have entered into the citric acid cycle but. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used.
In anaerobic respiration glucose breaks down to form alcohol and carbon dioxide with the release of small amount of energy.

Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy

Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
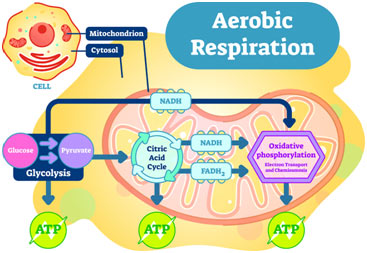
Cellular Respiration Types Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Biological Oxidation
Comments
Post a Comment